Sub-Systems of an Information system: EDP/MIS/DSS.
Electronic data processing (EDP)
Electronic data processing is also known as EDP, a frequently used term for automatic information processing. It uses the computers to collect, manipulate, record, classification and to summarize data. EPD can be described as the processing of data using electronic means such as computers, calculators, servers and other similar electronic data processing equipment. A computer is the best example of an EDP system. Use of a data processing system ensures accurate and rapid data processing. Electronic data processing equipment can have an inbuilt software or procedure to
EDP is the practice of processing, storing, retrieving, sharing and maintaining information electronically. There are many different ways to process data. The most common way of data processing is the machine learning technique called classification. It can be used for identifying issues in your data, finding patterns, and predicting outcomes. EDPs are computerized data processing systems that automate the collection, storage, manipulation, and retrieval of data. Text mining involves the process of categorizing, representing, and analysing huge amounts of text in order to derive useful information. The benefits of electronic data processing are numerous. Electronic data processing helps to reduce the development and maintenance cost of most business operations.
Electronic data processing offers various advantages over any other form as it is fast, accurate, reliable and flexible. E-commerce industry, banking services, record keeping, transaction data processing and any company dealing with real time data processing uses electronic data processing. Any data processing system comprises 4 basic components, these include hardware, software, procedure & person.
Methods of Electronic Data Processing:
- Time-sharing: In this processing method, many nodes connected to a CPU accessed central computer. A multi-user processing system controls the time allocation to each user. Each user can allocate the time slice in a sequence of the Central Processing Unit. The user should complete the task during the assigned time slice. If the user cannot finish the task, then the user can complete the task during another allocated time slice.
- Real-time processing: It Providing accurate and up-to-date information is the primary aim of real-time processing. It is possible when the computer processes the incoming data. It will give the immediate response to what may happen. It would affect the upcoming events. Making a reservation for train and airline seats are the best example for real-time processing.
- Online processing: In this processing method, the data is processed instantly. A communication link helps to connect the computer to the data input unit directly. The data input may include a network terminal or online input device. Online processing is mostly used for information research and recording.
- Multiprocessing: Multiprocessing is processing of more than one task that uses the different processors at the same time of the same computer. It is possible in network servers and mainframes. In this process, a computer may consist of more than one independent CPU. This makes data processing much faster.
- Multitasking: It is an essential feature of data processing. Working with different processors at the same time is called multitasking. In this process, the various tasks share the same processing resource. The operating systems in the multitasking process are time-sharing systems.
- Interactive processing: This method includes three types of functions. The following are the types of function:
- Peak detection
- Integration
- Quantitation
- Batch processing: Batch processing is a method of the process the organized data into divided groups. In this method, the processing data can be divided as a group over a required time period. The batch processing method allows the computer to perform different priorities for an interaction. This method is very unique and useful to process.
- Distributed processing: This method is usually used for remote workstations, since the remote workstations are connected to a big workstation. The customers get the better services from this process. In this process, the firms can distribute the use of geographical computers. The best example for this distributed processing method is ATMs. ATMs are connected to the banking system.
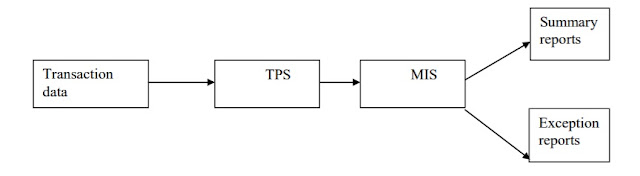
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS (MIS):
Fig: Interaction between TPS and MIS for Information Needs of an Organisation.
Decision Support System (DSS):
Decision support systems (DSS) are interactive software-based systems intended to help managers in decision-making by accessing large volumes of information generated from various related information systems involved in organizational business processes, such as office automation system, transaction processing system, etc.
DSS uses the summary information, exceptions, patterns, and trends using the analytical models. A decision support system helps in decision-making but does not necessarily give a decision itself. The decision makers compile useful information from raw data, documents, personal knowledge, and/or business models to identify and solve problems and make decisions.
Components of a DSS
Following are the components of the Decision Support System −
- Database Management System (DBMS)− To solve a problem the necessary data may come from internal or external database. In an organization, internal data are generated by a system such as TPS and MIS. External data come from a variety of sources such as newspapers, online data services, databases (financial, marketing, human resources).
-
Model Management System − It stores and accesses models that managers use to make decisions. Such models are used for designing manufacturing facility, analysing the financial health of an organization, forecasting demand of a product or service, etc.
- Support Tools − Support tools like online help; pulls down menus, user interfaces, graphical analysis, error correction mechanism, facilitates the user interactions with the system.
Types of DSS:
Following are some typical DSSs −
- Status Inquiry System− It helps in taking operational, management level, or middle level management decisions, for example daily schedules of jobs to machines or machines to operators.
- Data Analysis System− It needs comparative analysis and makes use of formula or an algorithm, for example cash flow analysis, inventory analysis etc.
- Information Analysis System− In this system data is analyzed and the information report is generated. For example, sales analysis, accounts receivable systems, market analysis etc.
- Accounting System− It keeps track of accounting and finance related information, for example, final account, accounts receivables, accounts payables, etc. that keep track of the major aspects of the business.
- Model Based System− Simulation models or optimization models used for decision-making are used infrequently and creates general guidelines for operation or management.
You might also like:
Procedural, Object-oriented and event driven Programming Languages (Visual Basic).