statements in c programming language
In the C programming language, statements are the building blocks of a program, representing individual executable instructions. A statement is typically terminated by a semicolon (;). C supports various types of statements, each serving a specific purpose within the program’s logic.
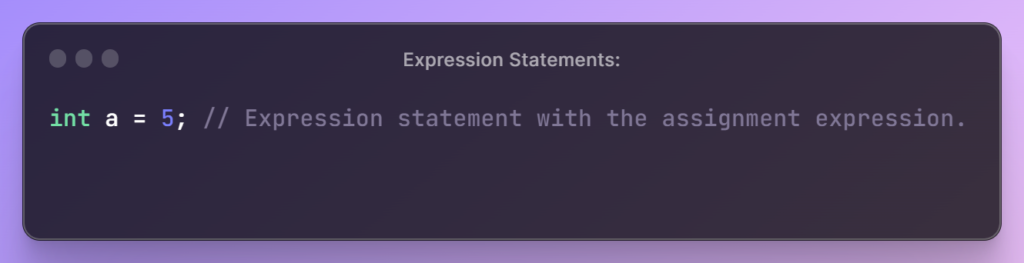
Expression Statements:
- The most common type, an expression statement consists of an expression followed by a semicolon. Expressions may involve variables, constants, and operators, and their evaluation results in a value.
Compound Statements (Blocks):
- A compound statement, also known as a block, is a group of statements enclosed within curly braces
{}. It allows multiple statements to be executed together, creating a scope for local variables.

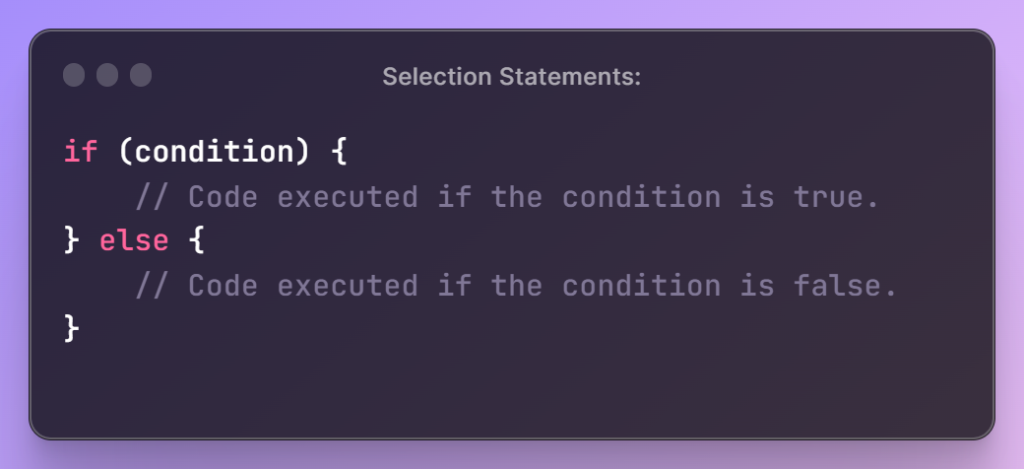
Selection Statements:
- Selection statements allow conditional execution of code based on a specified condition. The most common selection statement is the
if-elsestatement.
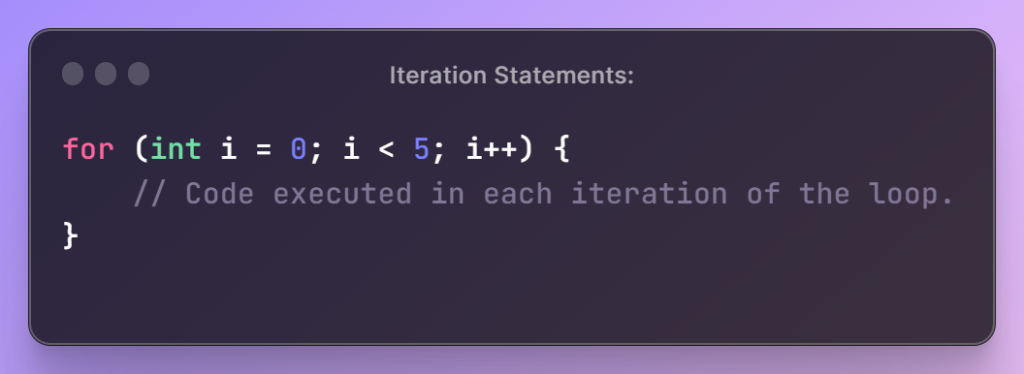
Iteration Statements:
- Iteration statements, or loops, enable repeated execution of a block of code while a specified condition holds true. Examples include
for,while, anddo-whileloops.
Jump Statements:
- Jump statements alter the flow of control in a program. Examples include
break(exits a loop),continue(skips the rest of a loop’s body), andreturn(ends the execution of a function).

A statement in a computer program carries out some action. There are three types of statements used in C & C++; they are:
-
Expression statement:
Ari expression statement consists of any valid C & C++ expression followed by a semicolon. The expression statement is used to evaluate a group of expressions.
For example,
x = y;
sum = x+y;
-
Compound Statement:
A group of valid C & C++ expressions placed within a (and) statement is called a compound statement.
For example;
{
a= b+c;
x=x*x;
y=a+x;
}
-
Control Statement:
Control statement is used for the program flow and to check the condition of the given expression or a constant. The keywords of the control statements are normally a predefined or reserved words and the programmer may not use them as ordinary variables.
For example
if (a>b){
______________________
______________________
}
While (condition is becoming true)
{
______________________
______________________
}
These fundamental statements in c programming language provide the structure and control flow necessary for expressing the logic of a C program. The combination of these statements in c programming language allows developers to create powerful and efficient algorithms to solve various computational problems.

